
VLAN Frame Tagging Protocols (ISL and dot1.q)
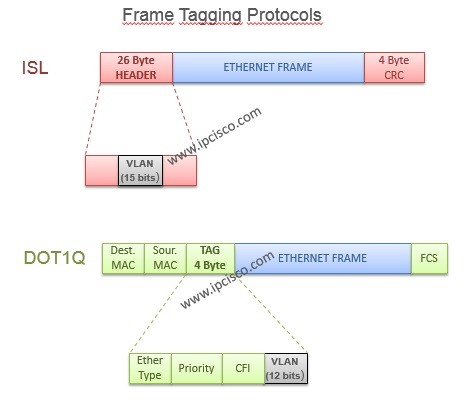
In this lesson, we will learn VLAN Frame Tagging Protocols detailly. In the next lessons, you can also check Cisco VLAN Configuration Examples. What are these VLAN Frame Tagging Protocols? Let’s see each of them. There are two types of frame tagging protocols. These are : – ISL(Inter-Switch Link) – dot1Q (or IEEE 802.1Q) These protocols can be configured manually or negotiated by DTP(Dynamic Trunking Protocol). DTP is a Cisco proprietary protocol. For VLAN Tagging Cisco, DTP can be used. ISL encapsulate the frame with a header (26 bytes) and trailer (4 bytes). So ISL increases the size of a frame 30 bytes. This protocol is a Cisco proprietary protocol and it is not supported on new Cisco devices. ISL support 1000 VLAN on a truk port. You can configure ISL on Cisco switches like below:
You May Also Like
-
Jun 30, 2025
Cisco Systems is one of the important vendors in information technology and network field. Many network engineers work with Cisco...
-
Jun 26, 2024
Network engineers need practice on routers and switches. They use different emulators and simulators to gain hands on experience on...
-
Mar 28, 2023
CCNP ENCOR 350-401 Exam is the required exam for CCNP ENCOR (Implementing Cisco Enterprise Network Core Technologies) or CCIE Enterprise...
Sign up to receive our latest updates
[mc4wp_form id=3101]
Get in touch
Call us directly?
+1 234 567 8910
Address
Howard Street, San Francisco
contact@eduma.com





