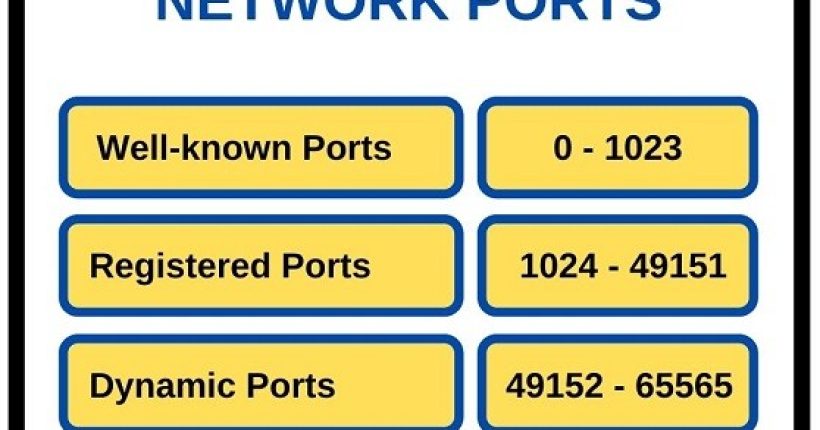

There are four types of PDU packets in IS-IS Protocol.
These IS-IS packets are :
– IS-IS Hello PDU (IIH)
– Link State PDU (LSP)
– Partial Sequence Number PDU (PSNP)
– Complete Sequence Number PDU (CSNP)
In IS-IS PDUs there is a TLV (Type, Length, Value) field. According to the need, these fields are added to the PDUs. This TLV field makes IS-IS extendable and it is the major advantage of IS-IS over OSPF. There are several TLVs in IS-IS packets. IS-IS Header always same, but according to the type of the packet, added TLV fields change.
TLVs are maximum 256 bytes and they contains sub-TLVs.

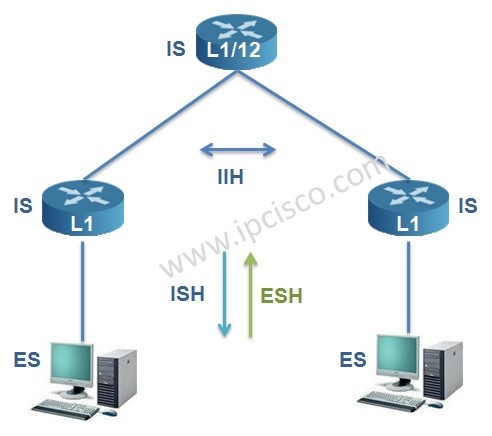
There are three types Hello PDUs in IS-IS Protocol:
ESH -> ES sent to IS
ISH -> IS sent to ES
IIH -> Between two ISs

IS-IS Hello interval is 10 seconds and the dead interval is 30 seconds by default.
In IS-IS Hello packet, 6 types of data can be included with TLVs. These are:
– Area Addresses TLV
– Padding TLV
– IP Interface Address TLV
– Authentication Information TLV
– Protocols Supported TLV
– Intermediate System Neighbors TLV
For more information about IS-IS TLVs, you can check Intermediate System-to-Intermediate System (IS-IS) TLVs article on Cisco Website.
IS-IS LSPs are like LSAs in OSPF and contains many information about the neighbour ISIS Routers and links. They are flooded periodically in IS-IS network. L1 and L2 PDUs use different formats LSPs are stored in IS-IS LSDBs. Seperate datababses are used for L1 and L2 LSPs. Each LSP has sequence number that shows its version.
In LSPs, below TLVs are supported: – Area Addresses TLV – Originating LSP Buffer Size TLV – Intermediate System Neighbors TLV – End System Neighbor TLV – Authentication Information TLV – Prefix Neighbor TLV – Protocols Supported TLV – IP Interface Address TLV – IP Internal Reachability Information TLV – IP External Reachability Information TLV
[sc name=”ContentRMessage”]
The other articles on IS-IS Protocol are below:
Routing With IS-IS Protocol – Part 1
Routing With IS-IS Protocol – Part 2 (IS-IS Addresses)
Routing With IS-IS Protocol – Part 3 (IS-IS Packet Types)
Routing With IS-IS Protocol – Part 4 (IS-IS Adjacency)
Routing With IS-IS Protocol – Part 5 (IS-IS versus OSPF)
You May Also Like
-
Mar 17, 2022
-
Jan 10, 2021
-
Jan 5, 2021
Sign up to receive our latest updates
Get in touch
Call us directly?
Address