
OSPFv2 Overview
OSPF (Open Shortest Path First) is a Link-State Routing Protocol. It is also Classless and an Open, Standard Protocol used by all vendors. OSPF uses Dijsktra Algortihm, a Shortest Path First Algorithm (SPF) to determine the best path to a destination network. In this lesson, we will focus on Open Shortest Path First and we will learn the details of this Routing Protocol.OSPF Tables
Open Shortest Path First provides neighborship between other OSPF routers by the help of OSPF messages. With these messages, different tables are built. And Open Shortest Path First routing mechanims works with these tables. Basically, there are three tables. These tables are :- Neighboring Table
- Topology Table
- Routing Table
Hierarchical Design and Area Types
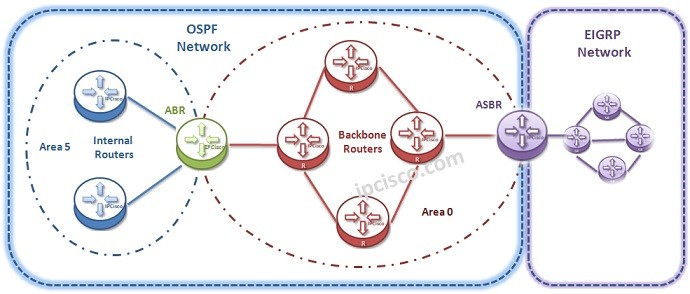
Open Shortest Path First has an hierarchical architecture. It uses “Areas” for hieararcy. There is a Backbone Area as Area 0 in the center for all OSPF Networks. Around this Backbone Area, Area 0, there are some other Areas. All these areas are connected to this Area 0. If there is a uncontinuous structure, Virtual-Links can be used to connect an area to the Backbone Area(Area 0). With this hierachical architecture of OSPF, you can divide your network into different small areas and by doing this, you can reduce overhead of this small areas. You can also use specific areas in OSPF network. These areas will be explain detailly later. Here, let’s only give the area types used in OSPF:- Standard Area
- Backbone Area (Area 0)
- Stub Area
- Not So Stubby Area (NSSA)
- Totally Stub Area
- Totally NSSA
OSPF Router Types
In OSPF Design there are different Router types. These router types are named according to their roles and their place of the network. Let’s see these router:- Internal Routers : Routers in a Single Area.
- Backbone Routers : Routers in Backbone Area (at least one interface).
- Area Border Routers(ABRs) : Routers have interfaces at least in two areas.
- Autonomus System Boundary Routers(ASBRs) : Routers connected to an another AS and redistribute external routes.
OSPF Administrative Distance Values
For Best Path selection, Administrative Distance(Preference) values are very important. Every Routing Protocol has an AD value. The Administrative Distance (Preference) of the Open Shortest Path First is 110 for Cisco devices. This is a little different for Alcatel-Lucent, Huawei and Juniper devices. They use Interneal and External Preference values for Open Shortest Path First. Preference value is 10 for Internal OSPF Routes and 150 for External OSPF Routes on the devices of these vendors.Open Shortest Path First Cost
Open Shortest Path First uses path Cost as its metric. Generally Bandwidth value is used as path Cost. AS a formula, the Cost is calculated like below in OSPF: Cost = Reference BW(default 10 000 000) / BWOSPF Versions
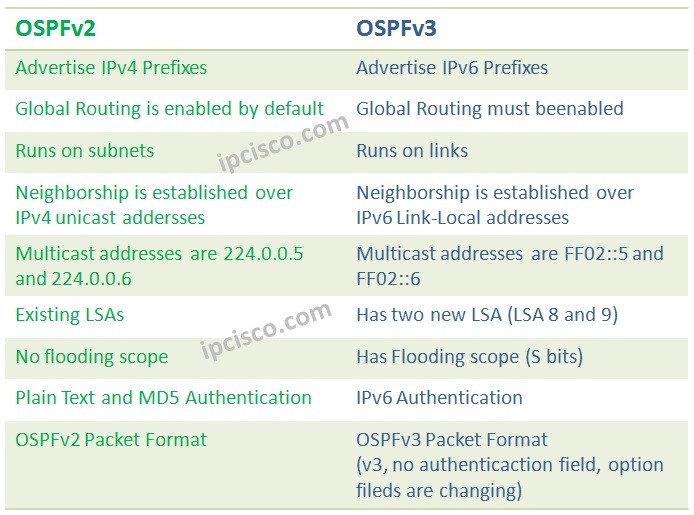
Protocols are developed and then they enhanced with new features. This new enhanced versions came with new versions. Open Shortest Path First also has different versions. There are two OSPF versions. These are:- OSPFv2
- OSPFv3
 In this article, we have talked about an overview of OSPFv2. In the following articles, we will explain this lesson more deeply. If you want to learn more about OSPFv3, you can check IPv6 Routing Protocols lesson.
In this article, we have talked about an overview of OSPFv2. In the following articles, we will explain this lesson more deeply. If you want to learn more about OSPFv3, you can check IPv6 Routing Protocols lesson.

You May Also Like
-
Jun 30, 2025
Cisco Systems is one of the important vendors in information technology and network field. Many network engineers work with Cisco...
-
Mar 13, 2025
What is NOS? A NOS (Network Operating System) is a special software that is designed for network equipment like router,...
-
Mar 28, 2023
CCNP ENCOR 350-401 Exam is the required exam for CCNP ENCOR (Implementing Cisco Enterprise Network Core Technologies) or CCIE Enterprise...
Sign up to receive our latest updates
[mc4wp_form id=3101]
Get in touch
Call us directly?
+1 234 567 8910
Address
Howard Street, San Francisco
contact@eduma.com





