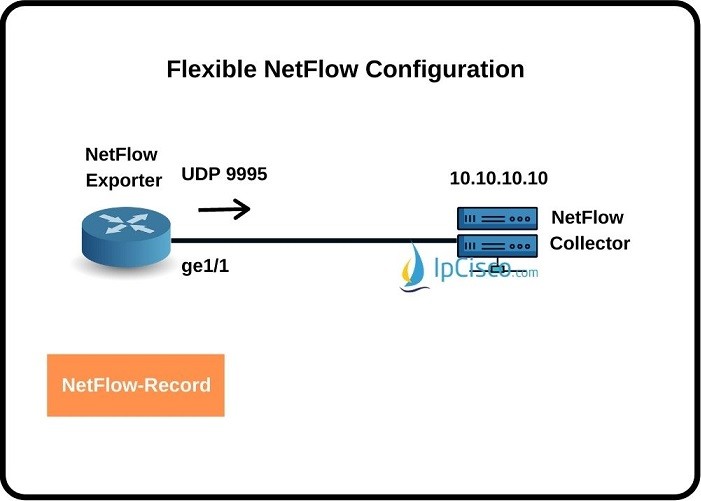

In this lesson, we will learn how to configure Flexible Netflow on Cisco Routers. We will see Cisco Flexible Netflow Configuration steps one by one with a configuration example. Before, we have also see Traditional NetFlow Configuration on Cisco Routers.
To configure Flexible Netflow Cisco, we will use five main steps. These steps and the commands that we will use in these steps are given below:
- Flow Record Configuration
- Flow Exporter Configuration
- Flow Sampler Configuration
- Flow Monitor Configuration
- Applying Flow Monitor To Interface
Flow Record Configuration
In this first step, we will create Flow Record with “flow record” command. Then we will add matching traffic and then we will mention the collect information. We will use Netflow-record as flow record name. Router(config) # flow record Netflow-Record Router(config-flow-record) # match ipv4 tos Router(config-flow-record) # match ipv4 protocol Router(config-flow-record) # match ipv4 source address Router(config-flow-record) # match ipv4 destination address Router(config-flow-record) # match transport source-port Router(config-flow-record) # match transport destination-port Router(config-flow-record) # match interface input Router(config-flow-record) # collect interface output Router(config-flow-record) # collect counter bytes Router(config-flow-record) # collect counter packets Router(config-flow-record) # exitFlow Exporter Configuration
In the second step, we will configure Flow Exporter. Here, as a destination, we will give the Flow Collector’s IP address and we will set source port. The configuration commands that we will use will be like below: Router(config)# flow exporter exporter-name Router(config-flow-exporter)# destination {hostname | ip-address} Router(config-flow-exporter) # source source-port Router(config-flow-exporter)# transport udp udp-port For our example, Netflow Exporter ip address will be 10.10.10.10. Oour source port will be ge1/1 and we will use the UDP port 9995. our configuration will be like below: Router(config) # flow exporter Netflow-Exporter Router(config-flow-exporter) # destination 10.10.10.10 Router(config-flow-exporter) # source ge1/1 Router(config-flow-exporter) # transport udp 9995 Router(config-flow-exporter) # exitFlow Sampler Configuration
In this step, firstly, we will create sampler with “sampler sampler-name” command. And then, we will determine the mode and sample number for window size. Router(config) # sampler SamplerXYZ Router(config-sampler) # mode {deterministic | random} 1 out-of window-size router(config-sampler)# end This is not a requirement but if we need to avoid traffic performance problem for high traffic, we can use Flow Sampler and limit number of monitored packets.Flow Monitor Configuration
In this step, we will configure Flow Monitor. We will take from one side and record to another side. We will also mention cache time out. router(config-flow-exporter)# flow monitor flow-monitor-name router(config-flow-monitor)# exporter exporter-name Router(config-flow-monitor) # record record-name Router(config-flow-monitor) # cache timeout active timeout-time router(config-flow-monitor)#end For our example, we will use Netflow-Montor as Flow monitor name and we will use Netflow-record as record name. Our cache timeout will be 60. Router(config) # flow monitor Netflow-Monitor Router(config-flow-monitor) # exporter Netflow-Exporter Router(config-flow-monitor) # record Netflow-Record Router(config-flow-monitor) # cache timeout active 60 Router(config-flow-monitor) # exitApplying Flow Monitor To Interface
In the last step, we will apply this Flow Monitor to the interface both input and output direction. We will apply Netflow-Monitor as Netflow Monitor to interface fa0/0 through both input and output direction. Router(config) # interface fa0/0 Router(config-if) # ip flow monitor Netflow-Monitor input Router(config-if) # ip flow monitor Netflow-Monitor output Router(config-if) # exit [sc name=”ContentRMessage”]You May Also Like
-
Jun 30, 2025
Cisco Systems is one of the important vendors in information technology and network field. Many network engineers work with Cisco...
-
Mar 13, 2025
What is NOS? A NOS (Network Operating System) is a special software that is designed for network equipment like router,...
-
Mar 28, 2023
CCNP ENCOR 350-401 Exam is the required exam for CCNP ENCOR (Implementing Cisco Enterprise Network Core Technologies) or CCIE Enterprise...
Sign up to receive our latest updates
[mc4wp_form id=3101]
Get in touch
Call us directly?
+1 234 567 8910
Address
Howard Street, San Francisco
contact@eduma.com





