
In this post, we will talk about an important and mostly used command of BGP. This command is used under the BGP process in the router and the usage is like below:
neighbor {ip-address | peer-group-name} next-hop-self
In the routing, route advertisement is a common term. And for the route advertisement, the next hop is common. A route is advertised via its next hop ip address. This means that, “You can come to me via this door”.
In BGP configuration, route advertisement is also done between external peers. During this advertisement, the non directly connected routers to this external peer, the IBGP peers, need to learn how to go to the advertised route. Because without any information, they can not go to an unknown place. And their routing table do not have this information.
To give this information to the IBGP peers, “next-hop-self” command is used. Let’s see how, with a configuration example.
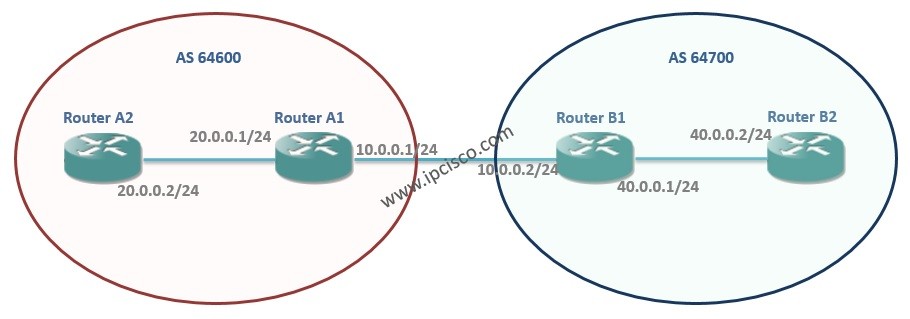
The topology used for this next-hop-self command is below:

BGP Next-Hop-Self Command
In this topology, Router A1 and Router B1 are external BGP peers. And the Router A2 and Router B2 are their internal BGP peers. Router A2 advertises its 20.0.0.0/24 network with the next hop 10.0.0.1 (ip address of Router A1’s external interface).Because of the fact that, this 10.0.0.1 ip address is not in the routing table of Router B2, it do not know this route.
[sc name=”ContentRMessage”]

You May Also Like
-
Jun 30, 2025
Cisco Systems is one of the important vendors in information technology and network field. Many network engineers work with Cisco...
-
Mar 13, 2025
What is NOS? A NOS (Network Operating System) is a special software that is designed for network equipment like router,...
-
Oct 18, 2022
In this EVE-NG VMware installation post, we will focus on one of the popular network emulators, EVE-NG. We will learn...
-
May 24, 2022
What is Cisco Live? Cisco Live is a traditional Cisco Event that exist for many years all over the word....
Sign up to receive our latest updates
[mc4wp_form id=3101]
Get in touch
Call us directly?
+1 234 567 8910
Address
Howard Street, San Francisco
contact@eduma.com





