
Packet Tracer RSTP Configuration
As you know, STP (Spanning Tree Protocol) is the key protocol of Switching world. With STP, link redundancy is provided and switching loops are avoided. STP has different versions. One of the STP version is RSTP (Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol). Like its name, RSTP (Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol) is the fastest converged version of STP. In this example, we will configure RSTP (Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol) with Packet Tracer.You can DOWNLOAD the Cisco Packet Tracer example with .pkt format At the End of This Lesson.
For all Packet Tracer Examples and Files, you can check Packet Tracer Labs Page.
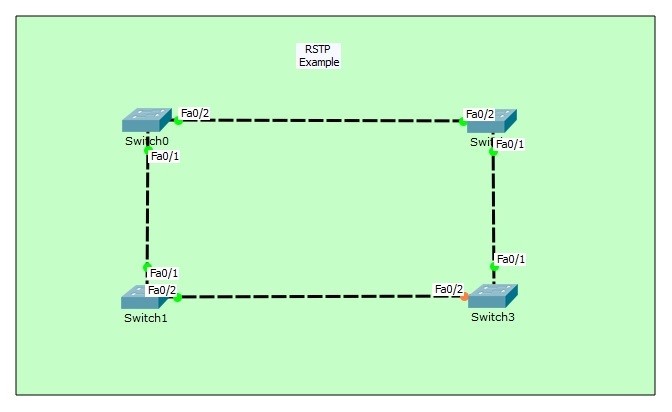
For our RSTP (Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol) example, we will use the below switching topology.

RSTP Confgiuration
Let’s start to configure RSTP (Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol) on Cisco Packet Tracer.
Switch0(config)# spanning-tree mode ? pvst Per-Vlan spanning tree mode rapid-pvst Per-Vlan rapid spanning tree mode
Switch0 (config)# spanning-tree mode rapid-pvst Switch0 (config)# end Switch0 # copy running-config startup-config
Switch1 (config)# spanning-tree mode rapid-pvst Switch1 (config)# end Switch1 # copy running-config startup-config
For all Packet Tracer Examples and Files, you can check Packet Tracer Labs Page.
Switch2 (config)# spanning-tree mode rapid-pvst Switch2 (config)# end Switch2 # copy running-config startup-config
Switch3 (config)# spanning-tree mode rapid-pvst Switch3 (config)# end Switch3 # copy running-config startup-config
RSTP Configuration Verification
Now, let’s verify our RSTP (Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol) on Packet Tracer.
Switch0# show spanning-tree VLAN0001 Spanning tree enabled protocol rstp Root ID Priority 32769 Address 0006.2A11.24CC This bridge is the root Hello Time 2 sec Max Age 20 sec Forward Delay 15 sec Bridge ID Priority 32769 (priority 32768 sys-id-ext 1) Address 0006.2A11.24CC Hello Time 2 sec Max Age 20 sec Forward Delay 15 sec Aging Time 20 Interface Role Sts Cost Prio.Nbr Type —————- —- — ——— ——– ——————————– Fa0/1 Desg FWD 19 128.1 P2p Fa0/2 Desg FWD 19 128.2 P2pHere, Switch0 is the root bridge. The ports of Switch0 are both in Designated role and both of them is in Forwarding State.
Switch0# show spanning-tree summary Switch is in rapid-pvst mode Root bridge for: default Extended system ID is enabled Portfast Default is disabled PortFast BPDU Guard Default is disabled Portfast BPDU Filter Default is disabled Loopguard Default is disabled EtherChannel misconfig guard is disabled UplinkFast is disabled BackboneFast is disabled Configured Pathcost method used is short Name Blocking Listening Learning Forwarding STP Active ———————- ——– ——— ——– ———- ———- VLAN0001 0 0 0 2 2 ———————- ——– ——— ——– ———- ———- 1 vlans 0 0 0 2 2As you can see above, our mode is in rapid-pvst mode. And this is for one VLAN, VLAN 1. We can also check the detailed RSTP (Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol) information with “show spanning-tree detail” command.
Switch0# show spanning-tree detail VLAN0001 is executing the rstp compatible Spanning Tree Protocol Bridge Identifier has priority of 32768, sysid 1, 0006.2A11.24CC Configured hello time 2, max age 20, forward delay 15 Current root has priority 32769 Topology change flag not set, detected flag not set Number of topology changes 0 last change occurred 00:00:00 ago from FastEthernet0/1 Times: hold 1, topology change 35, notification 2 hello 2, max age 20, forward delay 15 Timers: hello 0, topology change 0, notification 0, aging 300 Port 1 (FastEthernet0/1) of VLAN0001 is designated forwarding Port path cost 19, Port priority 128, Port Identifier 128.1 Designated bridge has priority 32769, address 0006.2A11.24CC Designated port id is 128.1, designated path cost 19 Timers: message age 16, forward delay 0, hold 0 Number of transitions to forwarding state: 1 Link type is point-to-point by default Port 2 (FastEthernet0/2) of VLAN0001 is designated forwarding Port path cost 19, Port priority 128, Port Identifier 128.2 Designated bridge has priority 32769, address 0006.2A11.24CC Designated port id is 128.2, designated path cost 19 Timers: message age 16, forward delay 0, hold 0 Number of transitions to forwarding state: 1 Link type is point-to-point by defaultLet’s check the show RSTP (Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol) on other switches.
Switch3# show spanning-tree VLAN0001 Spanning tree enabled protocol rstp Root ID Priority 32769 Address 0006.2A11.24CC Cost 38 Port 1(FastEthernet0/1) Hello Time 2 sec Max Age 20 sec Forward Delay 15 sec Bridge ID Priority 32769 (priority 32768 sys-id-ext 1) Address 000A.4139.1675 Hello Time 2 sec Max Age 20 sec Forward Delay 15 sec Aging Time 20 Interface Role Sts Cost Prio.Nbr Type —————- —- — ——— ——– ——— Fa0/1 Root FWD 19 128.1 P2p Fa0/2 Altn BLK 19 128.2 P2pInSwitch 3, one of the ports is in Forwarding State and the other is in Blocking State. The port role of Forwarding is “Root” role. The blocking port’s role is “Alternate”.
Switch2# show spanning-tree VLAN0001 Spanning tree enabled protocol rstp Root ID Priority 32769 Address 0006.2A11.24CC Cost 19 Port 2(FastEthernet0/2) Hello Time 2 sec Max Age 20 sec Forward Delay 15 sec Bridge ID Priority 32769 (priority 32768 sys-id-ext 1) Address 0040.0B3D.0E38 Hello Time 2 sec Max Age 20 sec Forward Delay 15 sec Aging Time 20 Interface Role Sts Cost Prio.Nbr Type —————- —- — ——— ——– ——— Fa0/1 Desg FWD 19 128.1 P2p Fa0/2 Root FWD 19 128.2 P2pInSwitch2, the ports are both in Forwarding States and the roles are Designated and Root. As you remember, here, the Root port is the closest port to Root Bridge. It is same for Switch1 too.
Switch1# show spanning-tree VLAN0001 Spanning tree enabled protocol rstp Root ID Priority 32769 Address 0006.2A11.24CC Cost 19 Port 1(FastEthernet0/1) Hello Time 2 sec Max Age 20 sec Forward Delay 15 sec Bridge ID Priority 32769 (priority 32768 sys-id-ext 1) Address 0060.4748.4B5A Hello Time 2 sec Max Age 20 sec Forward Delay 15 sec Aging Time 20 Interface Role Sts Cost Prio.Nbr Type —————- —- — ——— ——– ——— Fa0/1 Root FWD 19 128.1 P2p Fa0/2 Desg FWD 19 128.2 P2pYou can also test RSTP (Rapid Spanning Tree Protocol) states by deleting and then reconnecting the cables between switches. You will see that, the port states will rapidly go through Forwarding State.
You can check the other Packet Tracer Examples below:
Common Cisco Router Configuration Example on Packet Tracer
Router DHCP Configuration Example on Packet Tracer
VTP Configuration Example on Packet Tracer
VLAN Configuration Example on Packet Tracer
STP Configuration Example on Packet Tracer
RSTP Configuration with Packet Tracer
STP Portfast Configuration with Packet Tracer
Inter VLAN Routing Configuration on Packet Tracer
Switch Virtual Interface (SVI) Configuration with Packet Tracer
BGP Configuration Example on Packet Tracer
Port Security Configuration Example on Packet Tracer
RIP Configuration Example on Packet Tracer
CDP Configuration Example on Packet Tracer
OSPF Area Types Example on Packet Tracer (Standard and Backbone Areas)
OSPF External Routes Example on Packet Tracer
OSPF Area Types Example on Packet Tracer (Stub, NSSA, Totally Stubby, Totally NSSA Areas)
Standard Access-List Example on Packet Tracer
Extended Access-List Example on Packet Tracer
[sc name=”ContentRMessage”]
Tags:
You May Also Like
-
Jun 30, 2025
Cisco Systems is one of the important vendors in information technology and network field. Many network engineers work with Cisco...
-
Mar 13, 2025
What is NOS? A NOS (Network Operating System) is a special software that is designed for network equipment like router,...
-
Jun 26, 2024
Network engineers need practice on routers and switches. They use different emulators and simulators to gain hands on experience on...
Sign up to receive our latest updates
[mc4wp_form id=3101]
Get in touch
Call us directly?
+1 234 567 8910
Address
Howard Street, San Francisco
contact@eduma.com





