
Packet Tracer CDP Configuration
As we have talked about in the previous lesson, CDPis a Cisco proprietary Neighbor Discovery Protocol. In this article, we will discuss how to configure CDP in Cisco IOS, we will learn CDP Cisco Configuration. LLDP is a standard neighbour discovery protocol. In another lesson we will also configure LLDP.You can DOWNLOAD the Packet Tracer example with .pkt format HERE.
For all Packet Tracer Examples and Files, you can check Packet Tracer Labs Page.
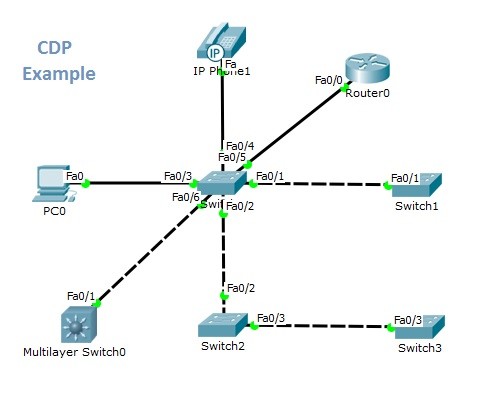
For our example, the below topology is used.

To enable CDP globally, use “cdp run” on the router configuration mode. To disable Cisco Discovery Protocol, we can use “no cdp run” command.
Switch(config)# cdp run Switch(config)# no cdp run
If this protocol is disabled globally and we can enable it on a specific interface. To enable CDP on a specific interface, use “cdp enable” command on the interface configuration mode. By default CDP is already enabled. You can also disable CDP by using “no cdp enable” command.
Switch(config-if)# cdp enable Switch(config-if)# no cdp enable
There are timers used in Cisco Discovery Protocol. The roles of these timers and default values are given below:
- CDP Timer: CDP advertisement time, hello (60 seconds by default)
- CDP Holdtime: CDP record holding time (120 seconds by default)
To configure cdp Hello time and Hold time, you can use the below commands. Time is mentioned as seconds.
Switch(config)# cdp timer 50 Switch(config)# cdp holdtime 100
To clear the CDP table, use the “clear cdp table” command.
Switch# clear cdp table
To verify CDP, you can use general CDP verification commands below:
Switch# show cdp Switch# show cdp interface Switch# show cdp neighbors Switch# show cdp entry Switch# show cdp traffic
In our topology, for the central switch, “show cdp neighbours” and “show cdp interface” command outputs are showed below.
Switch# show cdp neighbors Capability Codes: R – Router, T – Trans Bridge, B – Source Route Bridge S – Switch, H – Host, I – IGMP, r – Repeater, P – Phone Device ID Local Intrfce Holdtme Capability Platform Port ID IP Phone Fas 0/4 124 H P 7960 Switch Fas 0/6 124 3560 Fas 0/1 Switch Fas 0/2 124 S 2960 Fas 0/2 Router Fas 0/5 124 R C2800 Fas 0/0 Switch Fas 0/1 124 S 2950 Fas 0/1
For all Packet Tracer Examples and Files, you can check Packet Tracer Labs Page.
Switch# show cdp interface FastEthernet0/1 is up, line protocol is up Sending CDP packets every 60 seconds Holdtime is 180 seconds FastEthernet0/2 is up, line protocol is up Sending CDP packets every 60 seconds Holdtime is 180 seconds FastEthernet0/3 is up, line protocol is up Sending CDP packets every 60 seconds Holdtime is 180 seconds FastEthernet0/4 is up, line protocol is up Sending CDP packets every 60 seconds Holdtime is 180 seconds FastEthernet0/5 is up, line protocol is up Sending CDP packets every 60 seconds Holdtime is 180 seconds FastEthernet0/6 is up, line protocol is up Sending CDP packets every 60 seconds Holdtime is 180 seconds FastEthernet0/7 is down, line protocol is down Sending CDP packets every 60 seconds Holdtime is 180 seconds FastEthernet0/8 is down, line protocol is down Sending CDP packets every 60 seconds Holdtime is 180 seconds FastEthernet0/9 is down, line protocol is down Sending CDP packets every 60 seconds Holdtime is 180 seconds FastEthernet0/10 is down, line protocol is down Sending CDP packets every 60 seconds Holdtime is 180 seconds FastEthernet0/11 is down, line protocol is down Sending CDP packets every 60 seconds Holdtime is 180 seconds FastEthernet0/12 is down, line protocol is down Sending CDP packets every 60 seconds Holdtime is 180 seconds FastEthernet0/13 is down, line protocol is down Sending CDP packets every 60 seconds Holdtime is 180 seconds FastEthernet0/14 is down, line protocol is down Sending CDP packets every 60 seconds Holdtime is 180 seconds FastEthernet0/15 is down, line protocol is down Sending CDP packets every 60 seconds Holdtime is 180 seconds FastEthernet0/16 is down, line protocol is down Sending CDP packets every 60 seconds Holdtime is 180 seconds FastEthernet0/17 is down, line protocol is down Sending CDP packets every 60 seconds Holdtime is 180 seconds FastEthernet0/18 is down, line protocol is down Sending CDP packets every 60 seconds Holdtime is 180 seconds FastEthernet0/19 is down, line protocol is down Sending CDP packets every 60 seconds Holdtime is 180 seconds FastEthernet0/20 is down, line protocol is down Sending CDP packets every 60 seconds Holdtime is 180 seconds FastEthernet0/21 is down, line protocol is down Sending CDP packets every 60 seconds Holdtime is 180 seconds FastEthernet0/22 is down, line protocol is down Sending CDP packets every 60 seconds Holdtime is 180 seconds FastEthernet0/23 is down, line protocol is down Sending CDP packets every 60 seconds Holdtime is 180 seconds FastEthernet0/24 is down, line protocol is down Sending CDP packets every 60 seconds Holdtime is 180 seconds GigabitEthernet0/1 is down, line protocol is down Sending CDP packets every 60 seconds Holdtime is 180 seconds GigabitEthernet0/2 is down, line protocol is down Sending CDP packets every 60 seconds Holdtime is 180 seconds
In this article, we have talked about the configuration of Cisco Discovery Protocol (CDP) basically with Cisco Packet Tracer.
You can DOWNLOAD the Packet Tracer example with .pkt format HERE.
You can download “Packet Tracer” in Tools section.
[sc name=”ContentRMessage”]
You May Also Like
-
Jun 30, 2025
Cisco Systems is one of the important vendors in information technology and network field. Many network engineers work with Cisco...
-
Mar 13, 2025
What is NOS? A NOS (Network Operating System) is a special software that is designed for network equipment like router,...
-
Jun 26, 2024
Network engineers need practice on routers and switches. They use different emulators and simulators to gain hands on experience on...
Sign up to receive our latest updates
[mc4wp_form id=3101]
Get in touch
Call us directly?
+1 234 567 8910
Address
Howard Street, San Francisco
contact@eduma.com





