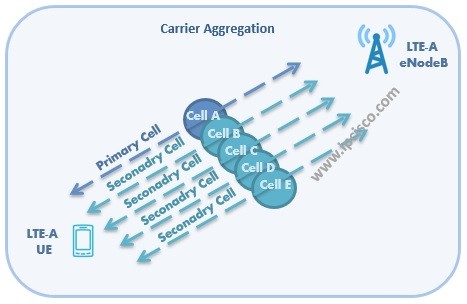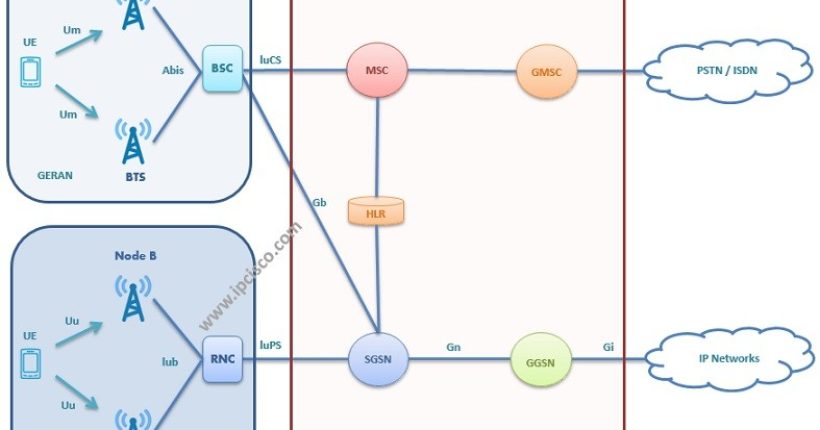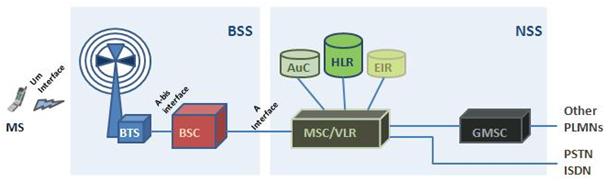

The evolution of the 2G technology to LTE technology is in three types:

- Technical evolution : The new network elements are developed with new technology
- Network Evolution : General functionality of network will change
- Service Evolution : Demand generated by the end user will increase
GSM (Global System for Mobile Communication)
GSM is an ETSI standard to describe the second generation(2G) digital cellular networks. The original name was “Groupe Spécial Mobile”. Uses circuit switched network. With its evolution and adding packet switched networks, new generation technologies GPRS, EDGE, UMTS and at last LTE is introduced. The basic GSM architecture is below. Here, as you can see GSM architecture is divided 4 subsystems:- Mobile Station (MS)
- Base station Subsystem (BSS) : Radio path control
- Network Subsystem (NSS) : Call control
- Network Management Subsystem (NMS) : Operation and maintenance
You May Also Like
-
Mar 17, 2022
Networking Certifications has served as a stepping stone for those seeking to advance their careers in Networking, h they are...
-
Nov 11, 2021
Wireless technology is evolving every day. From the beginning of wifi technology, a new standard has developed and release almost...
-
Jun 9, 2015
As you know after LTE, LTE-A (LTE Advanced) is the next step of mobile technology. In this article, I will...
-
Jun 9, 2015
As you know mobile telecommunication has evolved for years. With this evolution, new network elements were included or the existing...
Sign up to receive our latest updates
[mc4wp_form id=3101]
Get in touch
Call us directly?
+1 234 567 8910
Address
Howard Street, San Francisco
contact@eduma.com